24+ How To Find Initial Vertical Velocity !!
Vy = v * sin(α) Then, divide that number by 2 and write down the quotient you get. V y = v y0 − gt. Where v1 is the initial velocity. A man covers a distance of 100 m.
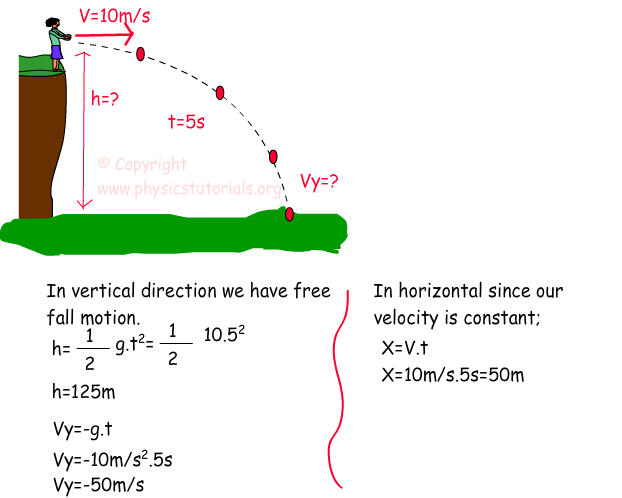
V y0 = initial velocity of the particle
25/06/2013 · to find initial velocity, start by multiplying the acceleration by the time. V 0 y = v 0 sin θ 0 = ( 30.0 m / s ) sin 45 ° = 21.2 m / s. Then, divide that number by 2 and write down the quotient you get. V y0 = initial velocity of the particle Also, the velocity of the particle changes from its initial value. 07/02/2012 · v = final velocity u = initial velocity s = displacment a = acceleration t = time elapsed these are all vector equations, so these apply for each component of velocity or displacment the first equation itexv=u + at/itex this tells you that the final velocity is equal to the initial velocity plus a term due to acceleration, which should be expected. Vx = v * cos(α) vertical velocity component: Therefore, to find the velocity of a particle in vertical displacement caused by the uniform acceleration of gravity is given by: Finally, subtract your first quotient … V (final velocity) = u + at. V y = v y0 − gt. Where v1 is the initial velocity. 30/10/2020 · the initial vertical velocity is the vertical component of the initial velocity:
Also, the velocity of the particle changes from its initial value. 30/10/2020 · the initial vertical velocity is the vertical component of the initial velocity: V (final velocity) = u + at. Therefore, to find the velocity of a particle in vertical displacement caused by the uniform acceleration of gravity is given by: Vx = v * cos(α) vertical velocity component:

V y = vertical velocity at time t.
V 0 y = v 0 sin θ 0 = ( 30.0 m / s ) sin 45 ° = 21.2 m / s. V y = v y0 − gt. A man covers a distance of 100 m. Where v1 is the initial velocity. This motion is called vertical projectile motion. Next, divide the distance by the time and write down that quotient as well. Also, the velocity of the particle changes from its initial value. Therefore, to find the velocity of a particle in vertical displacement caused by the uniform acceleration of gravity is given by: V (final velocity) = u + at. The following equation is used to calculate the initial velocity of an object. Then, divide that number by 2 and write down the quotient you get. Vx = v * cos(α) vertical velocity component: 07/02/2012 · v = final velocity u = initial velocity s = displacment a = acceleration t = time elapsed these are all vector equations, so these apply for each component of velocity or displacment the first equation itexv=u + at/itex this tells you that the final velocity is equal to the initial velocity plus a term due to acceleration, which should be expected.
V 0 y = v 0 sin θ 0 = ( 30.0 m / s ) sin 45 ° = 21.2 m / s. Therefore, to find the velocity of a particle in vertical displacement caused by the uniform acceleration of gravity is given by: Finally, subtract your first quotient … The following equation is used to calculate the initial velocity of an object. Vy = v * sin(α)

30/10/2020 · the initial vertical velocity is the vertical component of the initial velocity:
Vy = v * sin(α) A man covers a distance of 100 m. Also, the velocity of the particle changes from its initial value. 07/02/2012 · v = final velocity u = initial velocity s = displacment a = acceleration t = time elapsed these are all vector equations, so these apply for each component of velocity or displacment the first equation itexv=u + at/itex this tells you that the final velocity is equal to the initial velocity plus a term due to acceleration, which should be expected. Finally, subtract your first quotient … Vx = v * cos(α) vertical velocity component: Where v1 is the initial velocity. V y0 = initial velocity of the particle The following equation is used to calculate the initial velocity of an object. V 0 y = v 0 sin θ 0 = ( 30.0 m / s ) sin 45 ° = 21.2 m / s. This motion is called vertical projectile motion. Then, divide that number by 2 and write down the quotient you get. 30/10/2020 · the initial vertical velocity is the vertical component of the initial velocity:
24+ How To Find Initial Vertical Velocity !!. Next, divide the distance by the time and write down that quotient as well. Then, divide that number by 2 and write down the quotient you get. 30/10/2020 · the initial vertical velocity is the vertical component of the initial velocity: Also, the velocity of the particle changes from its initial value. V y0 = initial velocity of the particle
Posting Komentar untuk "24+ How To Find Initial Vertical Velocity !!"