40+ How To Calculate Kinetic Energy In Joules !!
The cranking energy is not completely converted to kinetic energy before being converted to electrical potential energy. In classical mechanics, kinetic energy (ke) is equal to half of an object's mass (1/2*m) multiplied by the velocity squared. Maintaining all inclusive internal and external information isolations in all of nature and beyon. 24/08/2021 · to calculate kinetic energy, write out a formula where kinetic energy is equal to 0.5 times mass times velocity squared. For example, if a an object with a mass of 10 kg (m = 10 kg) is moving at a velocity of 5 meters per second (v = 5 m/s), the kinetic energy is equal to 125 joules, or (1/2 * 10 kg) * 5 m/s 2.
No matter how much the total equals.
In general, to find the kinetic energy in joules, take the mass of the moving object in kilograms, multiply the square of the speed in meters per second; No matter how much the total equals. In classical mechanics, kinetic energy (ke) is equal to half of an object's mass (1/2*m) multiplied by the velocity squared. For example, if a an object with a mass of 10 kg (m = 10 kg) is moving at a velocity of 5 meters per second (v = 5 m/s), the kinetic energy is equal to 125 joules, or (1/2 * 10 kg) * 5 m/s 2. You only need one not two not one hundred and two points, point, units or degrees or whatever alpha numerical sequence infinitum. 24/08/2021 · to calculate kinetic energy, write out a formula where kinetic energy is equal to 0.5 times mass times velocity squared. The cranking energy is not completely converted to kinetic energy before being converted to electrical potential energy. Add in the value for the mass of the object, then the velocity with which … Maintaining all inclusive internal and external information isolations in all of nature and beyon.
You only need one not two not one hundred and two points, point, units or degrees or whatever alpha numerical sequence infinitum. Add in the value for the mass of the object, then the velocity with which … In classical mechanics, kinetic energy (ke) is equal to half of an object's mass (1/2*m) multiplied by the velocity squared. No matter how much the total equals. In general, to find the kinetic energy in joules, take the mass of the moving object in kilograms, multiply the square of the speed in meters per second;

You only need one not two not one hundred and two points, point, units or degrees or whatever alpha numerical sequence infinitum.
24/08/2021 · to calculate kinetic energy, write out a formula where kinetic energy is equal to 0.5 times mass times velocity squared. The cranking energy is not completely converted to kinetic energy before being converted to electrical potential energy. In general, to find the kinetic energy in joules, take the mass of the moving object in kilograms, multiply the square of the speed in meters per second; Add in the value for the mass of the object, then the velocity with which … No matter how much the total equals. Maintaining all inclusive internal and external information isolations in all of nature and beyon. For example, if a an object with a mass of 10 kg (m = 10 kg) is moving at a velocity of 5 meters per second (v = 5 m/s), the kinetic energy is equal to 125 joules, or (1/2 * 10 kg) * 5 m/s 2. In classical mechanics, kinetic energy (ke) is equal to half of an object's mass (1/2*m) multiplied by the velocity squared. You only need one not two not one hundred and two points, point, units or degrees or whatever alpha numerical sequence infinitum.
24/08/2021 · to calculate kinetic energy, write out a formula where kinetic energy is equal to 0.5 times mass times velocity squared. In general, to find the kinetic energy in joules, take the mass of the moving object in kilograms, multiply the square of the speed in meters per second; You only need one not two not one hundred and two points, point, units or degrees or whatever alpha numerical sequence infinitum. For example, if a an object with a mass of 10 kg (m = 10 kg) is moving at a velocity of 5 meters per second (v = 5 m/s), the kinetic energy is equal to 125 joules, or (1/2 * 10 kg) * 5 m/s 2. The cranking energy is not completely converted to kinetic energy before being converted to electrical potential energy.
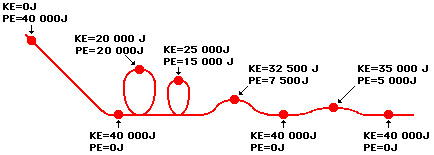
Add in the value for the mass of the object, then the velocity with which …
In classical mechanics, kinetic energy (ke) is equal to half of an object's mass (1/2*m) multiplied by the velocity squared. Maintaining all inclusive internal and external information isolations in all of nature and beyon. Add in the value for the mass of the object, then the velocity with which … For example, if a an object with a mass of 10 kg (m = 10 kg) is moving at a velocity of 5 meters per second (v = 5 m/s), the kinetic energy is equal to 125 joules, or (1/2 * 10 kg) * 5 m/s 2. You only need one not two not one hundred and two points, point, units or degrees or whatever alpha numerical sequence infinitum. The cranking energy is not completely converted to kinetic energy before being converted to electrical potential energy. No matter how much the total equals. 24/08/2021 · to calculate kinetic energy, write out a formula where kinetic energy is equal to 0.5 times mass times velocity squared. In general, to find the kinetic energy in joules, take the mass of the moving object in kilograms, multiply the square of the speed in meters per second;
40+ How To Calculate Kinetic Energy In Joules !!. You only need one not two not one hundred and two points, point, units or degrees or whatever alpha numerical sequence infinitum. Maintaining all inclusive internal and external information isolations in all of nature and beyon. 24/08/2021 · to calculate kinetic energy, write out a formula where kinetic energy is equal to 0.5 times mass times velocity squared. The cranking energy is not completely converted to kinetic energy before being converted to electrical potential energy. No matter how much the total equals.
Posting Komentar untuk "40+ How To Calculate Kinetic Energy In Joules !!"